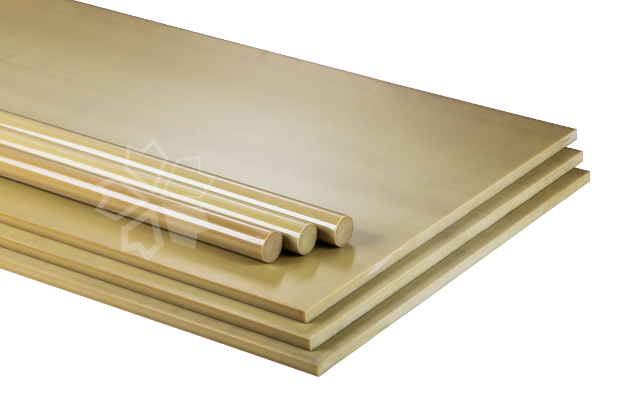

PEI(Ultem®2300) - 30% GLASS FIBER
Polyetherimide, an amorphous polymer with imine bonds and ether bonds in its molecular structure, shows transparent
amber in materials. Ultem®2300 is a 30% glass fiber reinforced polyetherimide resin produced by SABIC.
Since visible light could get through the polyetherimide, the agglomeration of glass fibers in the final product is clear. Zero Engineering uses "flowing dynamic-distribution technology" to produce GF30-PEI sheets and rods, helping the surface of material smooth and fiber-hidden; while the glass fiber in the final product is even-dispersed with good isotropy. The trademark of this series is ZEAMBER®.
Since visible light could get through the polyetherimide, the agglomeration of glass fibers in the final product is clear. Zero Engineering uses "flowing dynamic-distribution technology" to produce GF30-PEI sheets and rods, helping the surface of material smooth and fiber-hidden; while the glass fiber in the final product is even-dispersed with good isotropy. The trademark of this series is ZEAMBER®.
DETAILS
PERFORMANCE
- Typical non-crystalline resin, the highest glass transition temperature can reach 217℃
- Excellent mechanical properties under high temperatures
- Excellent thermal resistance, remain physical stable even in steam
- Excellent radiation resistance and UV resistance
- Excellent flame retardant (UL94V-0)
- Excellent electrical performance (loss-less, insulated)
- Resistant to gasoline, aliphatic hydrocarbons, alcohols as well as weak acids and bases
APPLICATIONS
- Electrical and electronic components, such as various connectors and sockets, OA equipment components;
- Semiconductor-manufactured equipment, heat-insulated parts;
- Food production equipment, steam cleaning equipment, medical equipment (steam resistant)
ATTENTIONS
- It may generate cracks (environmental stress cracking) if there are any organic solvents in cutting fluids. To ensure safety we highly recommend not to use the cutting fluids with any organic solvents.
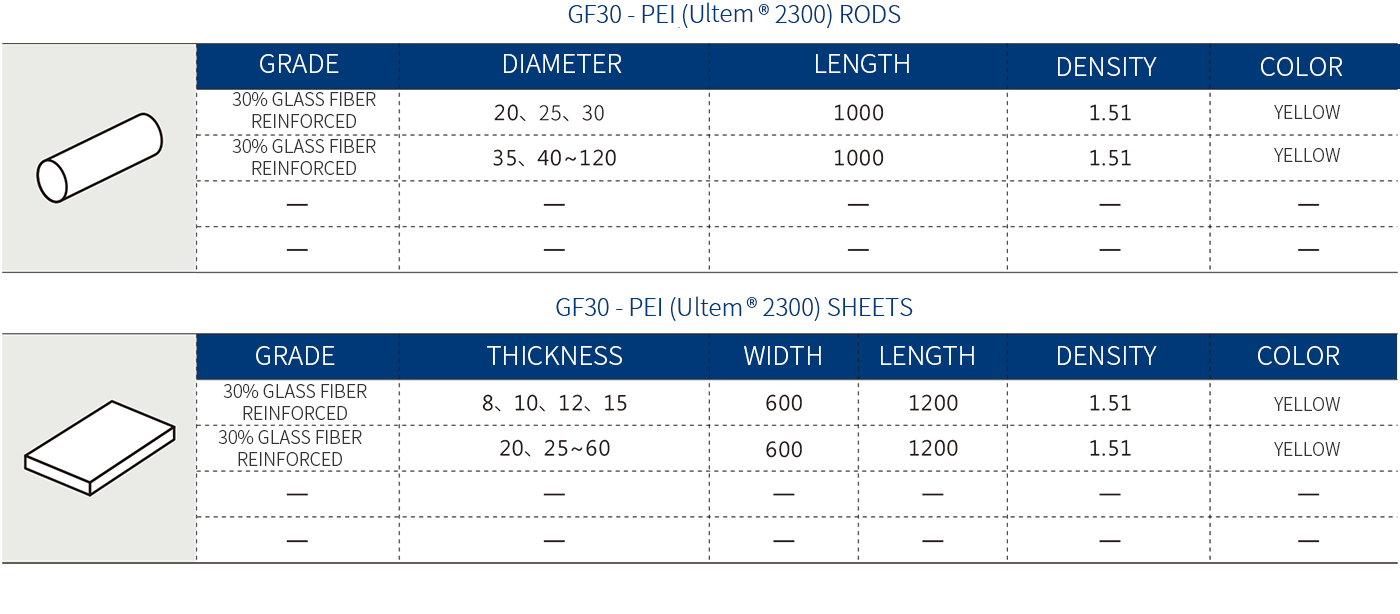
SPECIFICATIONS (mm, g/cm³)
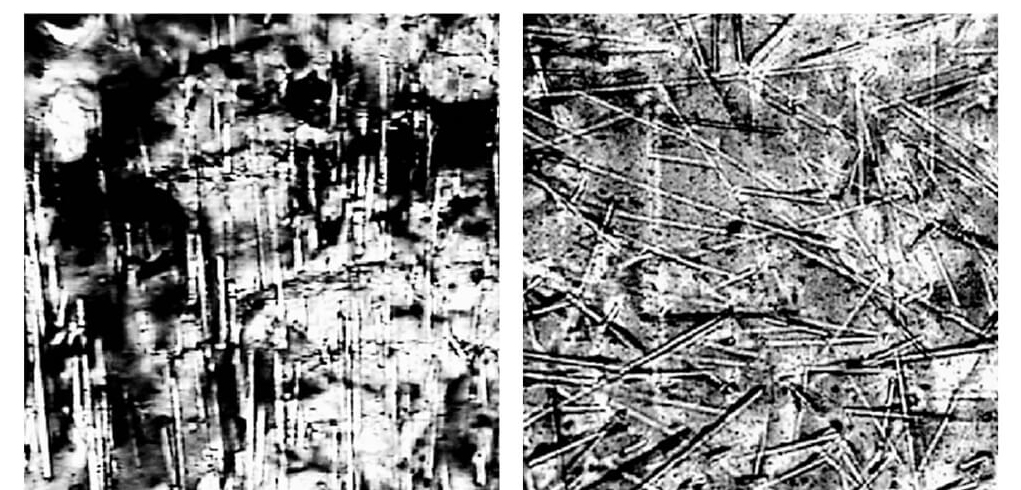
Getting a thin cut by a precision cutting machine and putting it under an optical microscope, we can observe the properties of the glass fiber. The fiber orientation is clear with a "Ⅱ" shape we show in the left figure, which indicates the anisotropy in the final product. But if it is even-mixed in a "W" shape as the right figure, then it shows the isotropy of the final product. Zero Engineering uses mixing-distribution technology and flowing distribution technology to achieve the stable isotropy of each product by even-mixing the glass fiber.


